Views: 1045

Flame retardant PVC tarpaulin is a special type of polyester fabric combined with PVC and fire-resistant additives. Unlike regular tarps, it slows down or stops fire from spreading, making it essential for places where fire safety is critical.When fire touches it:
✅ Slows down flames
✅ Stops burning when fire source is removed
✅ Protects what’s underneath
What’s Inside?
Flame retardant PVC tarpaulin is manufactured through a specialized process that involves:
- Base Material: High-strength polyester canvas that provides structural integrity
- PVC: Coated or laminated polyvinyl chloride (PVC) layer
- Flame Retardant Additives: Specific chemical compounds added during manufacturing
- Additional Additives: Accelerators, mildew inhibitors, anti-aging agents, and anti-static agents
| Component | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Polyester Fabric Base | Makes it strong and tear-proof |
| PVC Plastic | Makes it waterproof & flexible |
| Fire-Stop Chemicals | Prevents flames from spreading |
| Extra Protectors | Fights UV rays, mold & aging |
| Core Technology and Materials | ||
| Antimony Trioxide (Sb₂O₃) | Smoke Reduction | Dripping Control |
| Added to the PVC formulation to boost flame suppression. | Reduce toxic fume generation by up to 50% during fire exposure. | Reduced calcium carbonate formulation minimizes melt-dripping behavior. |
| Works with halogen compounds to form protective char barriers during combustion. | Minimize release of hazardous chemicals (including HCl gas). | Eliminates secondary fire hazards from falling molten material. |
| Significantly increases oxygen index (LOI) to achieve self-extinguishing properties. | Create clearer evacuation pathways in emergency scenarios. | Maintains fabric structural integrity at high temperatures. |
️ Where it’s used?
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Transport | Truck/train covers, cargo protection |
| Construction | Temporary shelters, scaffolding covers, debris containment |
| Events | Festival tents, stage backdrops, exhibition dividers |
| Storage | Warehouse covers, machinery protection |
| Public Spaces | Hospital barriers, school safety installations |
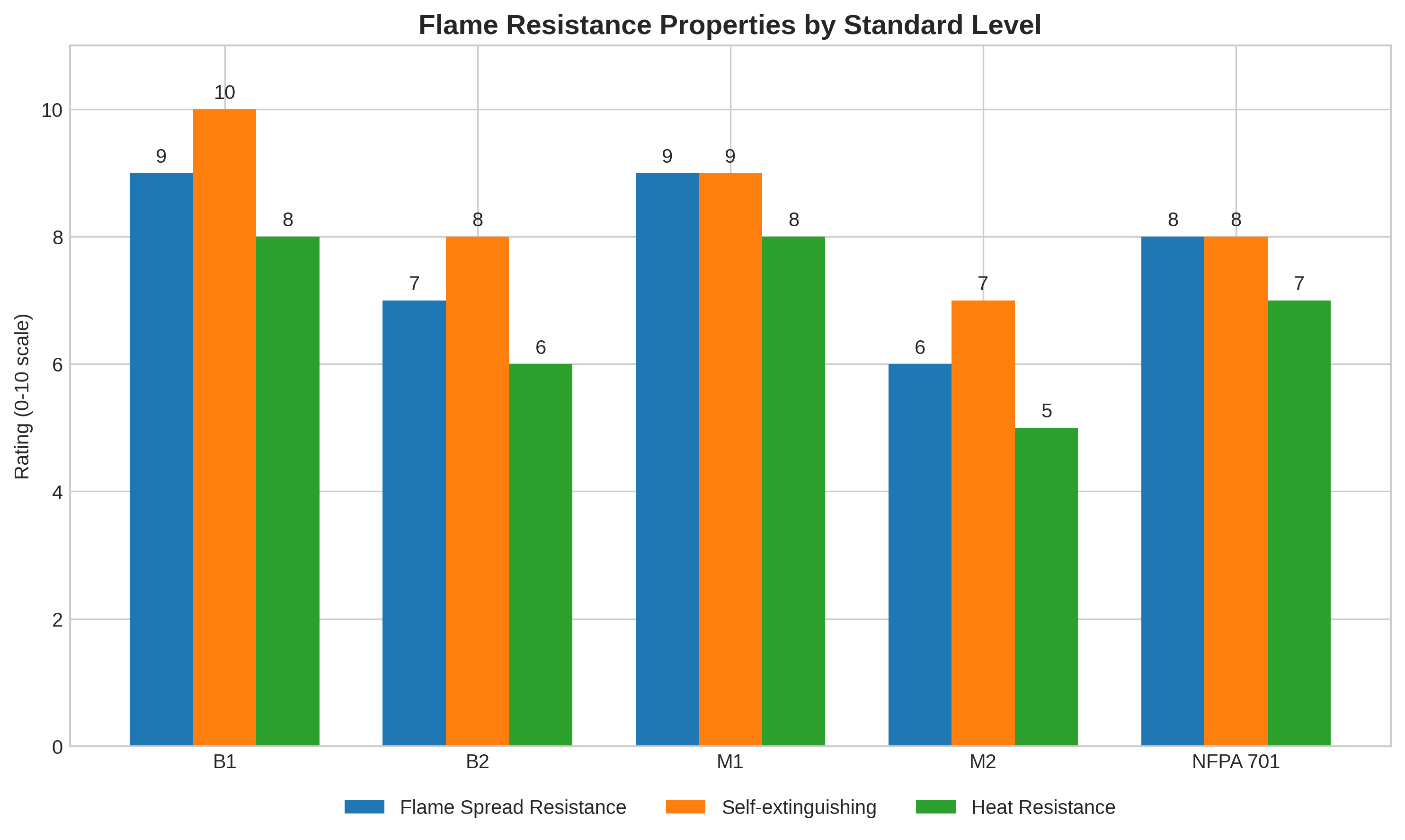
Global Safety Standards
| Standard | Country/Region | Key Classifications |
| Euroclasses (EN13501-1) | European Union | A1-F, s1-s3, d0-d2 |
| M Classification | France | M0-M4 |
| B Classification (DIN4102) | Germany | B1-B3 |
| NFPA 701 | United States | Test Method 1 & 2 |
| AS/NZS 1530 | Australia/New Zealand | Part 1-4 |
| Key Tests: How fast fire spreads / How long it keeps burning / How much smoke it makes | ||
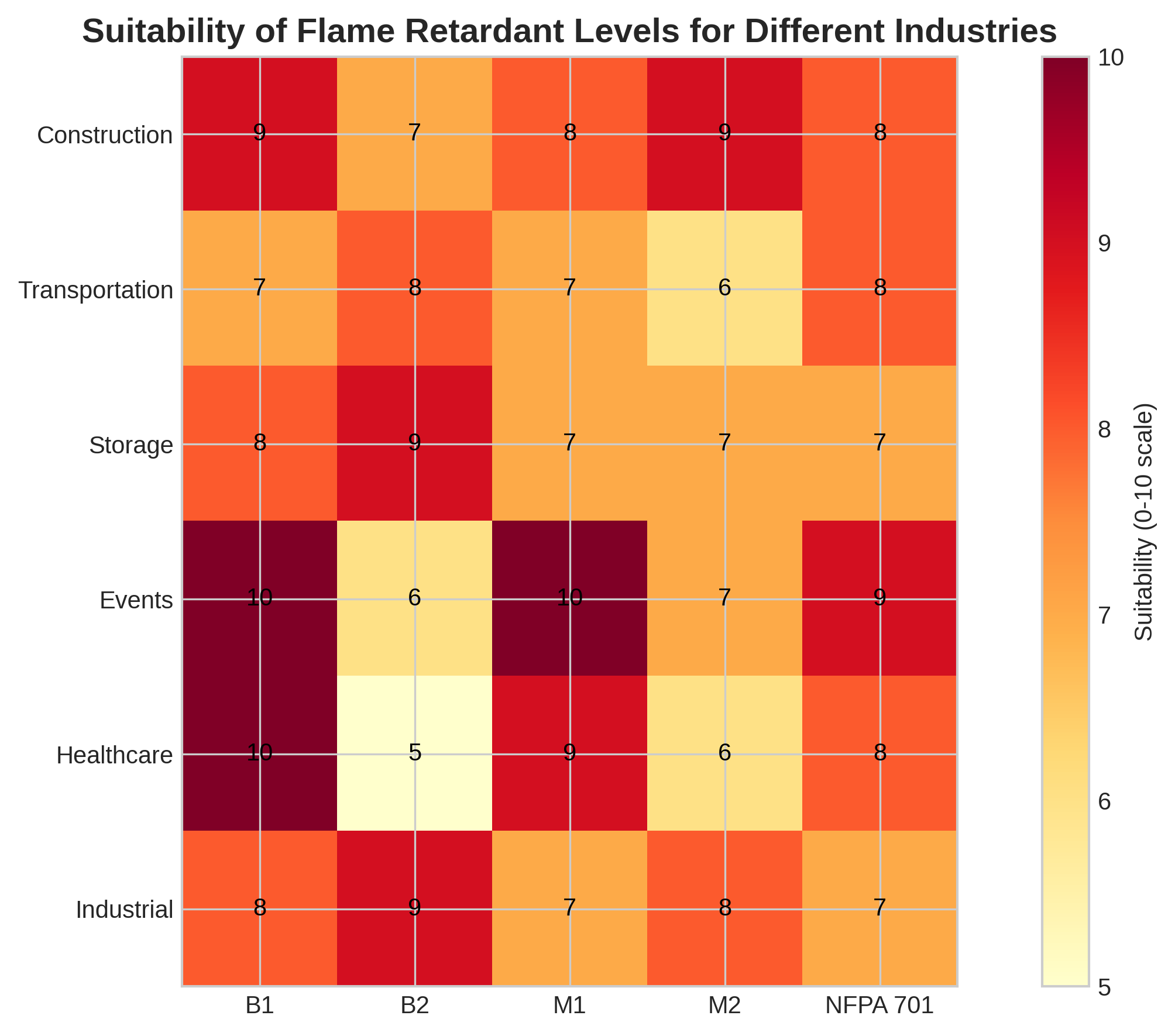
Flame Retardant Levels and Requirements
| Level | Description | Requirements |
| B1 | Fire retardant, self-extinguishing | Difficult to ignite, limited flame spread |
| B2 | Normally flammable, self-extinguishing | Less fire resistant than B1 |
| M1 | Non-flammable combustible materials | Excellent fire resistance, low flammability |
| M2 | Flammable materials with low flammability | Medium fire resistance |
| NFPA 701 Test 1 | For materials ≤700g/m², single-layer fabrics | Pass flame propagation test |
| NFPA 701 Test 2 | For plastic films, vinyl-coated fabrics | Pass flame propagation test for heavier materials |
Choosing Your Protection Level
| Fire Danger Level | Best Standard | Good For… |
|---|---|---|
| High risk | B1 or NFPA 701 Method 2 | Welding areas, chemical storage |
| Medium risk | NFPA 701 Method 1 | Event tents, truck covers |
| Basic protection | General flame retardant | Temporary covers, indoor use |
Applications of Different Flame Retardant Level Materials
| Level | Common Applications | Industry Sectors |
| B1 | Public buildings, exhibition halls, theaters, hospitals | Construction, Events, Healthcare |
| B2 | General industrial use, warehouses, temporary structures | Industrial, Storage, Transportation |
| M1 | Public buildings, high-risk environments, theaters | Events, Entertainment, Public facilities |
| M2 | Commercial buildings, standard requirements | Commercial, Industrial |
| NFPA 701 | Commercial buildings, public spaces in the US | Commercial, Public facilities, Events |